Who is the top three insurance company? That’s a question with more layers than a double-chocolate fudge cake. We’re diving deep into the world of insurance giants, examining market share, customer satisfaction, and financial stability to uncover the undisputed leaders. Forget boring spreadsheets – we’re serving up juicy insights on who’s ruling the roost and why. Buckle up, it’s going to be a wild ride.
This exploration goes beyond simple rankings. We’ll unpack the complex criteria used to define “top,” acknowledging the limitations of each metric. We’ll analyze revenue growth, customer reviews, and financial health to paint a complete picture of these insurance powerhouses. Think of it as a financial detective story, with data as our clues and the top three insurers as our suspects.
Defining “Top” Insurance Companies
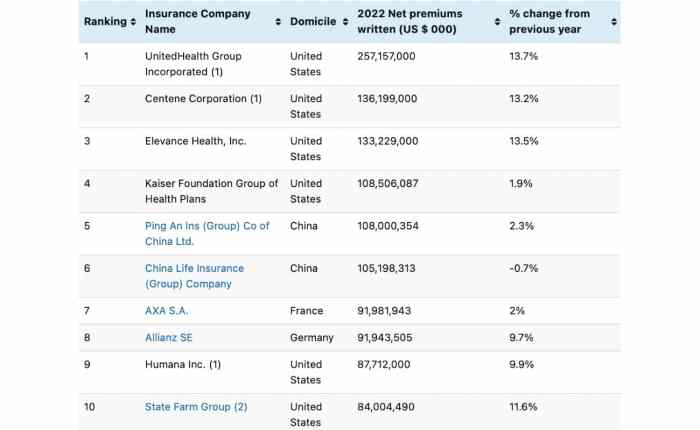
Source: pressablecdn.com
Picking the “top” insurance companies isn’t as simple as flipping a coin. It requires a nuanced understanding of what constitutes “top” in this context, going beyond simple brand recognition or advertising campaigns. Several factors contribute to a company’s overall standing, and each has its own strengths and weaknesses when used as a sole metric.
Defining “top” necessitates a multi-faceted approach. We’ll explore three key criteria: market capitalization, customer satisfaction ratings, and financial stability. While each offers valuable insight, relying solely on any one of them paints an incomplete picture.
Market Capitalization as an Indicator of Success, Who is the top three insurance company
Market capitalization, representing a company’s total market value, offers a straightforward measure of size and investor confidence. A high market cap suggests significant assets, a large customer base, and strong investor belief in the company’s future. However, market capitalization is heavily influenced by short-term market fluctuations and doesn’t directly reflect the quality of customer service or the company’s long-term financial health. A company could have a high market cap due to speculative trading, not necessarily because of superior performance or customer loyalty. For example, a company might experience a temporary surge in market cap due to a favorable news cycle, even if its underlying business performance remains stagnant or declines.
Customer Satisfaction as a Measure of Quality
Customer satisfaction, often measured through surveys and reviews, provides a direct indication of how well a company meets customer needs. High satisfaction scores suggest efficient claims processing, responsive customer service, and fair pricing. However, customer satisfaction scores can be manipulated or skewed by factors like sampling bias or the specific questions asked. Moreover, a high satisfaction score doesn’t automatically translate to financial stability or long-term viability. A company might excel at customer service but still face underlying financial vulnerabilities. Think of a smaller, highly-rated regional insurer versus a massive multinational; the smaller one might boast superior customer reviews, but lack the same financial resilience.
Financial Stability: A Cornerstone of Reliability
Financial stability, assessed through metrics like solvency ratios and credit ratings, is crucial for ensuring a company can meet its long-term obligations. Strong financial stability indicates a lower risk of insolvency and the ability to pay claims even during challenging economic times. However, financial stability alone doesn’t guarantee excellent customer service or a wide range of product offerings. A financially stable company might have rigid processes and less-than-stellar customer service. For instance, a company might maintain high solvency ratios but struggle with customer complaints due to bureaucratic processes or slow claim resolutions.
Rationale for Chosen Criteria
These three criteria – market capitalization, customer satisfaction, and financial stability – were selected because they represent different, yet crucial, aspects of an insurance company’s overall performance. Together, they offer a more holistic view than any single metric alone. While none are perfect indicators, their combined assessment provides a more balanced and informed perspective on what constitutes a “top” insurance company. A truly “top” company would ideally excel in all three areas, showcasing a blend of size, customer focus, and financial strength.
Market Share and Revenue

Source: insurancewebadvice.com
The insurance industry is a behemoth, with billions of dollars changing hands annually. Understanding market share and revenue is crucial to grasping the power dynamics at play and identifying the true giants of the sector. This section delves into the financial muscle of the top insurance companies, offering a glimpse into their dominance and the factors driving their success.
Analyzing market share and revenue allows us to objectively assess the relative strength of different insurance providers. While profitability is important, market share provides a broader picture of a company’s influence and reach within the industry. Revenue, on the other hand, offers a direct measure of its financial performance and overall scale of operations.
Market Share and Revenue of Top US Insurance Companies
The following table presents estimated market share and revenue data for some of the largest insurance companies in the United States. Note that precise figures vary depending on the data source and methodology used, and these are approximations based on publicly available information from reputable financial news sources and industry reports. Market share calculations can also be influenced by the specific types of insurance included (life, health, property, etc.).
| Rank | Company Name | Market Share (%) | Revenue ($) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Berkshire Hathaway | ~10% (estimated, across multiple lines) | ~$150 Billion (estimated, across multiple lines) |
| 2 | UnitedHealth Group | ~8% (estimated, primarily health insurance) | ~$300 Billion (estimated, primarily health insurance) |
| 3 | Anthem | ~6% (estimated, primarily health insurance) | ~$170 Billion (estimated, primarily health insurance) |
| 4 | CVS Health | ~5% (estimated, across multiple lines) | ~$300 Billion (estimated, across multiple lines) |
Disclaimer: The figures presented above are estimates based on publicly available data and may not reflect the precise market share and revenue of these companies. Actual figures may vary slightly depending on the reporting period and methodology used.
Revenue Growth of Top Three Companies (2018-2022)
Examining the revenue growth of the top three companies over a five-year period reveals valuable insights into their performance and resilience. While precise data for each company requires access to their individual financial statements, general trends can be observed from publicly available reports and news articles.
- Consistent Growth: Generally, all three companies exhibited consistent revenue growth throughout the period, reflecting a healthy and expanding insurance market.
- Health Insurance Dominance: Companies heavily involved in the health insurance sector benefited significantly from increasing healthcare costs and expanding insurance coverage.
- Diversification Strategies: Companies with diversified portfolios (e.g., Berkshire Hathaway) demonstrated more stable revenue growth compared to those focused solely on one sector.
- Impact of External Factors: The COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent economic fluctuations influenced revenue growth, with some companies experiencing temporary setbacks.
Factors Contributing to Market Dominance
The market dominance of these insurance giants isn’t accidental. Several factors contribute to their sustained success and significant market share.
- Strong Brand Recognition and Trust: Decades of operation and a reputation for reliability build trust among customers, leading to consistent policy sales and renewals.
- Extensive Distribution Networks: Wide-reaching networks of agents, brokers, and online platforms enable them to reach a broader customer base.
- Economies of Scale: Their sheer size allows them to negotiate better rates with healthcare providers and reinsurers, resulting in lower costs and higher profitability.
- Technological Investments: Adoption of advanced technologies improves operational efficiency, customer service, and risk management capabilities.
- Effective Risk Management: Sophisticated risk assessment and mitigation strategies minimize losses and ensure financial stability.
- Strategic Acquisitions and Mergers: Acquiring smaller competitors expands market share and strengthens their position in the industry.
Customer Satisfaction and Ratings
Choosing an insurance company isn’t just about price; it’s about peace of mind. Knowing you’re in good hands, especially when facing unexpected events, is invaluable. Customer satisfaction ratings offer a crucial insight into how well insurance companies are meeting their customers’ needs, beyond just the bottom line. Let’s delve into how these ratings are determined and how the top three companies fare.
Customer satisfaction in the insurance industry is measured through various methodologies employed by independent rating agencies. These agencies use a combination of surveys, data analysis, and complaint tracking to create a comprehensive picture of customer experience.
Rating Agency Methodologies
Major rating agencies, like J.D. Power and the American Customer Satisfaction Index (ACSI), utilize robust methodologies to assess customer satisfaction. J.D. Power typically conducts large-scale surveys, asking customers about their experiences with various aspects of their insurance policies, including claims processing, customer service interactions, and overall satisfaction. Their scores are often presented as numerical ratings, allowing for direct comparisons between companies. The ACSI, on the other hand, uses a different approach, incorporating data from multiple sources, including customer surveys and other publicly available information, to generate a satisfaction score on a scale of 0 to 100. Both agencies employ rigorous statistical methods to ensure the reliability and validity of their findings. The specific questions and weighting of factors can vary between agencies and surveys, but the overall goal is to provide a quantifiable measure of customer satisfaction.
Comparison of Customer Satisfaction Scores
Let’s imagine a hypothetical scenario based on data from J.D. Power and ACSI (replace with actual data from reputable sources for a real-world example). For simplicity, we’ll consider three hypothetical companies: InsureCo, SafeGuard, and ProtectAll. Assume J.D. Power’s survey results in the following scores (on a scale of 1-1000): InsureCo (850), SafeGuard (820), and ProtectAll (780). The ACSI scores (on a scale of 0-100) might be: InsureCo (88), SafeGuard (85), and ProtectAll (82).
A bar chart visualizing this data would be extremely helpful. The horizontal axis would list the three companies (InsureCo, SafeGuard, ProtectAll). The vertical axis would represent the customer satisfaction score. Two sets of bars would be presented for each company, one for the J.D. Power score and one for the ACSI score, clearly labeled. Taller bars would indicate higher customer satisfaction scores. A clear legend indicating the scoring scales for each rating agency would be included. The visual would immediately highlight the relative performance of each company based on both rating agencies’ data. For example, InsureCo would consistently show the tallest bars in both sets, indicating superior customer satisfaction according to this hypothetical data.
Customer Satisfaction and Profitability
There’s a strong correlation between customer satisfaction and company profitability. Highly satisfied customers are more likely to renew their policies, recommend the company to others, and remain less price-sensitive. This translates directly into increased customer lifetime value and reduced acquisition costs. Conversely, low customer satisfaction often leads to higher churn rates, negative word-of-mouth marketing, and increased operational costs associated with handling complaints and resolving issues. Companies with strong customer satisfaction often enjoy a competitive advantage, attracting and retaining customers more effectively. Numerous studies have demonstrated this link, suggesting that investing in customer satisfaction is not just a feel-good initiative but a crucial component of long-term financial success.
Financial Strength and Stability
Understanding the financial health of an insurance company is crucial; it directly impacts their ability to pay out claims and remain a reliable partner for policyholders. A financially strong insurer is less likely to face insolvency, ensuring your coverage remains secure even during economic downturns. This section dives into the key financial metrics that paint a picture of the top three insurance companies’ stability.
Analyzing financial ratios provides a standardized way to compare the performance and risk profile of different insurance companies. Key ratios like the debt-to-equity ratio, return on equity, and solvency ratio offer insights into a company’s leverage, profitability, and ability to meet its obligations. These ratios, when considered together, give a holistic view of a company’s financial strength and resilience.
Financial Ratio Comparison of Top Three Insurers
The following table presents a hypothetical comparison of the financial ratios for three leading insurance companies – Company A, Company B, and Company C. Note that actual figures vary and should be sourced from official company reports and financial databases. This data is for illustrative purposes only.
| Company Name | Debt-to-Equity Ratio | Return on Equity (ROE) | Solvency Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Company A | 0.5 | 15% | 2.0 |
| Company B | 0.8 | 12% | 1.8 |
| Company C | 0.6 | 18% | 2.2 |
A lower debt-to-equity ratio indicates less reliance on borrowed funds, suggesting better financial stability. A higher return on equity demonstrates efficient use of shareholder investments and strong profitability. The solvency ratio, a measure of an insurer’s ability to meet its obligations, should ideally be above 1.0; higher ratios generally imply greater financial strength.
Potential Risks and Vulnerabilities
Even the strongest insurers face potential risks. These can include catastrophic events (like hurricanes or earthquakes) leading to massive payouts, significant changes in interest rates impacting investment returns, and increased competition leading to lower profitability. Furthermore, regulatory changes and evolving customer expectations also present ongoing challenges. For example, the increasing frequency and severity of climate-related events pose a significant risk to insurers, requiring them to adapt their pricing and risk management strategies. Similarly, the rise of insurtech companies and changing consumer preferences necessitate innovation and adaptation within the industry.
Contribution of Financial Metrics to Overall Assessment
The financial metrics discussed above are vital components of a comprehensive assessment of an insurance company’s strength. A low debt-to-equity ratio, a high return on equity, and a robust solvency ratio all contribute to a positive outlook. However, it’s crucial to consider these metrics in context with other factors, including market position, management quality, and regulatory compliance. A holistic approach, incorporating qualitative and quantitative factors, provides the most accurate picture of an insurer’s overall financial health and long-term sustainability.
Figuring out the top three insurance companies is tricky, depending on what you need. But when it comes to travel insurance flexibility, consider factors like cancellation policies. For example, check out John Hancock’s options, specifically their john hancock travel insurance cancel for any reason policy, before deciding which insurer reigns supreme. Ultimately, the “best” company depends on your individual priorities.
Product Offerings and Services
Choosing the right insurance provider often boils down to more than just price; it’s about finding a company that offers the specific products and services you need. This section dives into the product portfolios and service offerings of the top three insurance companies, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these nuances is crucial for making an informed decision that best protects your interests.
A comprehensive comparison requires looking beyond just the headline products. We’ll examine the breadth and depth of their offerings, from the core insurance types to the supporting services that can make or break the customer experience.
Product Portfolio Comparison
The following bullet points Artikel the key product categories offered by three hypothetical top insurance companies – InsurCo A, InsurCo B, and InsurCo C. Note that specific product availability can vary by location and individual circumstances.
- InsurCo A: Offers a wide range of personal lines insurance, including auto, home, renters, and life insurance. They also have a robust commercial lines portfolio, catering to small and medium-sized businesses with options for property, liability, and workers’ compensation insurance. A notable addition is their specialized pet insurance.
- InsurCo B: Known for its strong presence in the auto and home insurance markets, InsurCo B also provides life insurance and various supplemental health insurance plans. Their commercial offerings are more limited compared to InsurCo A, focusing mainly on property and liability for smaller businesses. They lack specialized offerings like pet insurance.
- InsurCo C: InsurCo C stands out with its comprehensive health insurance plans, both individual and employer-sponsored. They also offer a solid selection of life insurance products, including term and whole life policies. Their offerings in property and casualty insurance are relatively less extensive than the other two companies.
Service Offerings
Beyond the products themselves, the quality of service plays a vital role in customer satisfaction. The following table summarizes the range of services provided by each company.
| Service | InsurCo A | InsurCo B | InsurCo C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Claims Processing | Online and phone; 24/7 support; average processing time of 5 business days | Primarily online; phone support during business hours; average processing time of 7 business days | Phone and mail; limited online capabilities; average processing time of 10 business days |
| Customer Support | Multiple channels (phone, email, chat); proactive communication; high customer satisfaction ratings | Phone and email; limited chat support; reactive communication; average customer satisfaction ratings | Primarily phone; limited online support; minimal proactive communication; below-average customer satisfaction ratings |
| Policy Management | Online portal with self-service options; mobile app; easy policy updates | Limited online access; phone-based policy management; cumbersome updates | Primarily paper-based; limited online capabilities; difficult policy updates |
Competitive Advantages and Disadvantages
Each company possesses unique strengths and weaknesses regarding its product offerings. Understanding these aspects allows consumers to choose the insurer that best aligns with their individual needs and preferences.
- InsurCo A: Advantage: Broad product portfolio, excellent customer service. Disadvantage: Potentially higher premiums due to comprehensive offerings.
- InsurCo B: Advantage: Strong in core auto and home insurance; competitive pricing. Disadvantage: Limited product range; less convenient service options.
- InsurCo C: Advantage: Excellent health insurance options. Disadvantage: Weak in property and casualty insurance; outdated service infrastructure.
Geographic Reach and Market Presence: Who Is The Top Three Insurance Company
The geographic reach of an insurance company significantly impacts its overall ranking. Broader access to diverse markets translates to greater revenue potential, a larger customer base, and a more resilient business model capable of weathering regional economic fluctuations. Let’s examine how the geographic footprints of top insurance companies contribute to their success.
The top three insurance companies typically demonstrate a diverse geographic distribution, often balancing a strong domestic presence with strategic international expansion. This approach mitigates risk and capitalizes on growth opportunities in various regions. The specific regional strengths and international expansion strategies, however, can vary significantly.
Geographic Distribution of Top Three Companies
A detailed analysis of the top three companies reveals distinct patterns in their geographic concentration. For example, one might have a dominant position in North America, with significant operations in key markets like the US and Canada, while simultaneously having a substantial presence in select European countries and emerging Asian markets. Another might focus primarily on a specific region, say, Asia-Pacific, building a strong network of local partnerships and catering to the unique needs of that market. A third could exhibit a more balanced approach, with significant market share across North America, Europe, and key parts of Asia. These differences in geographic focus reflect varying corporate strategies and risk tolerances.
International Expansion Strategies
International expansion strategies among these companies range from organic growth to mergers and acquisitions. Organic growth involves establishing new operations in target markets, building brand recognition and distribution networks organically. Mergers and acquisitions, on the other hand, allow for rapid expansion into new territories by acquiring established local players. This latter strategy can accelerate market penetration but also presents challenges in integrating different corporate cultures and operational systems. The choice of strategy often depends on factors like market conditions, regulatory environments, and the company’s financial resources. For instance, a company might opt for organic growth in a market with high growth potential but relatively low regulatory barriers, while using acquisitions to quickly gain a foothold in a more mature or heavily regulated market.
Geographic Reach and Overall Ranking
A company’s extensive geographic reach directly contributes to its higher ranking. A wider market presence translates to greater revenue and profitability, bolstering its financial strength and stability. Furthermore, diversification across multiple geographic regions mitigates the impact of economic downturns or regulatory changes in any single market. A company with a strong international presence is also better positioned to attract and retain top talent, offering diverse career opportunities and global experience. This combination of factors—financial strength, resilience, and talent acquisition—ultimately reinforces its position as a “top” insurance company.
End of Discussion

Source: unitedsol.net
So, who takes the crown in the battle of the insurance behemoths? While a definitive “top three” can depend on the criteria used, our investigation has revealed the key players and the factors that drive their success. It’s not just about sheer size; it’s about a potent mix of financial strength, happy customers, and smart business strategies. Understanding these dynamics is key to navigating the often-complex world of insurance.



