Smartphones brands are the driving force behind the mobile revolution, shaping the way we communicate, access information, and interact with the world. From their humble beginnings to the sleek, powerful devices we carry today, smartphones have undergone a remarkable transformation, driven by relentless innovation and fierce competition.
This exploration delves into the fascinating world of smartphone brands, examining their history, market dominance, product differentiation, target audiences, pricing strategies, and brand reputation. We’ll explore how brands navigate the ever-evolving landscape of technology, consumer preferences, and industry dynamics, while also considering sustainability and ethical considerations.
Smartphone Brand History
The smartphone industry has undergone a dramatic evolution since its inception, driven by technological advancements, fierce competition, and shifting consumer preferences. From the early days of clunky devices to the sleek, powerful smartphones of today, the journey has been marked by key milestones and innovations that have shaped the industry as we know it.
Major Milestones and Innovations
The development of the smartphone can be traced back to the late 1990s and early 2000s, with several key milestones paving the way for the modern device.
- 1994: IBM Simon Personal Communicator, often considered the first true smartphone, combined mobile phone and PDA functionalities, allowing users to make calls, send faxes, and access email.
- 1996: Nokia 9000 Communicator, a more advanced device with a full QWERTY keyboard and internet access, was a significant step forward in smartphone development.
- 2007: The launch of the Apple iPhone marked a turning point in the industry. Its intuitive touchscreen interface, sleek design, and robust app ecosystem revolutionized the way people interacted with mobile devices.
- 2008: Google released the Android operating system, which quickly gained popularity for its open-source nature and flexibility. This paved the way for a diverse range of Android-powered smartphones from various manufacturers.
- 2010: The introduction of the iPad by Apple ushered in the era of tablets, further blurring the lines between smartphones and other computing devices.
- 2011: The launch of the Samsung Galaxy S II, with its powerful hardware and high-resolution display, solidified Samsung’s position as a leading smartphone manufacturer.
- 2014: The rise of mobile gaming and the increasing demand for high-performance devices led to the development of powerful processors and high-resolution displays, further enhancing the smartphone experience.
- 2016: The introduction of dual-camera systems and artificial intelligence (AI) features marked a significant shift in smartphone photography and user experience.
- 2019: The development of 5G technology, with its faster speeds and lower latency, opened up new possibilities for mobile connectivity and applications.
Smartphone Brand Mergers, Acquisitions, and Spin-offs
The smartphone industry has witnessed a number of mergers, acquisitions, and spin-offs over the years, shaping the competitive landscape and influencing the trajectory of the industry.
- 2008: Google acquired Android, an open-source mobile operating system, and quickly became a major player in the smartphone industry.
- 2011: Microsoft acquired Nokia’s mobile phone business, hoping to gain a foothold in the smartphone market. However, the acquisition proved unsuccessful and Microsoft eventually sold its mobile phone business to FIH Mobile Limited in 2016.
- 2016: Lenovo acquired Motorola Mobility from Google, adding another brand to its portfolio.
- 2017: HMD Global, a Finnish company, acquired the rights to the Nokia brand for smartphones and feature phones.
- 2020: LG Electronics announced its exit from the smartphone market, ending its long-standing presence in the industry.
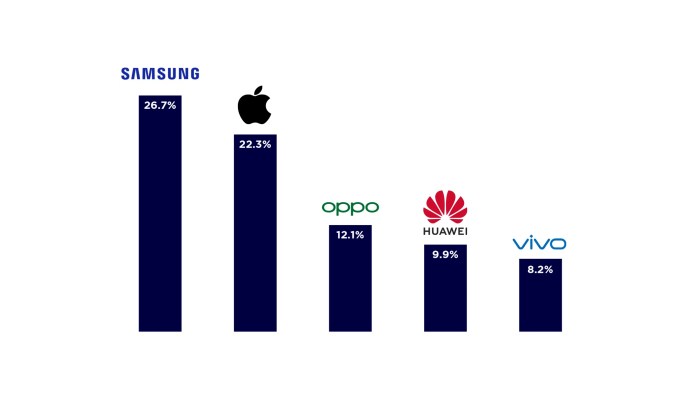
The smartphone market is a dynamic and competitive landscape, with a handful of brands dominating the global scene. Understanding market share and dominance is crucial for comprehending the industry’s power dynamics and predicting future trends.
The global smartphone market is dominated by a few major players. Samsung and Apple consistently hold the top two positions, followed by other prominent brands like Xiaomi, Oppo, and Vivo.
| Brand | Market Share (%) | Key Strengths |
|---|---|---|
| Samsung | 23.0 | Wide range of devices, strong brand recognition, strong presence in emerging markets, competitive pricing |
| Apple | 16.0 | Premium brand image, strong ecosystem, loyal customer base, high profit margins |
| Xiaomi | 14.0 | Value-for-money devices, strong online presence, aggressive marketing strategies, expanding global footprint |
| Oppo | 10.0 | Focus on camera technology, stylish designs, strong presence in Southeast Asia and China, innovative features |
| Vivo | 9.0 | Emphasis on camera and audio features, strong brand recognition in China, expanding global reach, partnerships with celebrities |
Regional Dominance
While some brands like Samsung and Apple enjoy global dominance, others have a stronger presence in specific regions. For instance, Xiaomi enjoys significant market share in China and India, while Oppo and Vivo are particularly popular in Southeast Asia.
“Regional preferences and market dynamics play a crucial role in determining brand dominance.”
Several factors contribute to the market share of leading smartphone brands:
- Brand Reputation and Image: Strong brand reputation and positive brand image are essential for attracting customers and building loyalty.
- Product Innovation and Features: Offering innovative features and high-quality products is crucial for staying competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
- Pricing Strategy: A competitive pricing strategy is essential for reaching a wide customer base and maximizing market penetration.
- Marketing and Distribution: Effective marketing campaigns and a robust distribution network are essential for reaching potential customers and generating sales.
- Ecosystem and Services: Offering a comprehensive ecosystem of services, such as app stores, cloud storage, and payment platforms, can enhance customer experience and brand loyalty.
Pricing Strategies and Value Proposition
Smartphone pricing strategies are complex, influenced by factors such as target audience, features, and competition. Brands often employ different approaches to position themselves in the market and appeal to specific consumer segments. The value proposition offered by each brand is crucial, as it defines the perceived worth of the product in relation to its price.
Pricing Strategies
Smartphone brands adopt a variety of pricing strategies to cater to diverse market segments and achieve their business objectives.
- Premium Pricing: This strategy involves setting high prices for smartphones with advanced features, premium materials, and brand prestige. Brands like Apple, Samsung, and Google utilize this strategy to target affluent consumers who prioritize innovation and brand exclusivity. For example, Apple’s iPhone Pro models are priced significantly higher than its standard iPhone models, reflecting their advanced features and high-end design.
- Value Pricing: This strategy focuses on offering competitive prices for smartphones with features that meet the needs of budget-conscious consumers. Brands like Xiaomi, Realme, and OnePlus are known for their value-oriented pricing, offering high-performance features at affordable prices. This strategy aims to attract price-sensitive customers who are looking for a good balance between features and cost.
- Competitive Pricing: This strategy involves matching or slightly undercutting the prices of competitors to maintain market share and attract price-sensitive consumers. Brands like Samsung, Oppo, and Vivo often employ this strategy, adjusting their prices to stay competitive in the market. This approach can be particularly effective in highly competitive segments, where consumers are sensitive to price differences.
- Cost-Plus Pricing: This strategy involves adding a markup to the cost of production to determine the selling price. This approach is often used by manufacturers who have a strong understanding of their production costs. While this strategy ensures profitability, it can make it difficult to compete with brands that offer more aggressive pricing.
Value Proposition
The value proposition of a smartphone brand encompasses the benefits and features that it offers to consumers.
- Premium Brands: Premium brands often focus on innovation, design, and brand image. They offer high-performance features, premium materials, and a seamless user experience. The value proposition for premium brands is often based on the prestige and exclusivity associated with the brand.
- Value Brands: Value brands prioritize affordability and features. They aim to offer the best possible features at a competitive price, attracting consumers who are looking for a good value for their money. Value brands often emphasize features like long battery life, high-resolution displays, and powerful processors.
Balancing Affordability, Features, and Perceived Value
Smartphone brands face a delicate balancing act when setting prices. They need to consider the cost of production, the target audience, and the competitive landscape.
- Affordability: Brands must ensure that their products are priced within reach of their target audience. This is particularly important in emerging markets, where price sensitivity is high.
- Features: Smartphones need to offer a compelling set of features to justify their price. Brands need to strike a balance between providing essential features and adding premium features that differentiate their products.
- Perceived Value: The perceived value of a smartphone is influenced by factors such as brand reputation, design, and marketing. Brands can enhance perceived value through effective branding, marketing campaigns, and customer service.
Marketing and Advertising Strategies
Smartphone brands employ a wide range of marketing and advertising strategies to reach their target audience and build brand awareness. These strategies encompass both traditional and digital channels, leveraging various tactics to capture consumer attention and drive sales.
Digital Marketing
Digital marketing has become an indispensable tool for smartphone brands to engage with their audience online.
- Search Engine Optimization (): Optimizing websites and content for search engines like Google helps brands appear higher in search results, driving traffic to their online platforms. For instance, Samsung leverages to ensure its flagship devices like the Galaxy S series rank prominently in search results for relevant s.
- Social Media Marketing: Social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter are essential for building brand awareness, interacting with customers, and promoting new products. Brands use engaging content, influencer marketing, and targeted advertising to reach their target audience on these platforms. For example, Apple uses its social media channels to showcase the sleek design and innovative features of its iPhones, generating excitement and anticipation for new releases.
- Content Marketing: Creating valuable and informative content such as blog posts, articles, and videos helps brands establish thought leadership and build trust with their audience. This strategy is particularly effective for attracting tech-savvy consumers who seek in-depth information about smartphones. Xiaomi, for example, publishes articles and videos on its website and social media channels, providing insights into its technology and product development process.
- Email Marketing: Email marketing remains a valuable tool for reaching target audiences with personalized messages about new products, promotions, and updates. Brands can segment their email lists to ensure that messages are relevant to specific customer interests. Google uses email marketing to send notifications about updates to its Android operating system and to promote its Pixel smartphone line.
Social Media Campaigns
Social media campaigns are a powerful way for smartphone brands to create buzz and generate engagement with their target audience.
- Hashtag Challenges: Brands often launch hashtag challenges on social media platforms to encourage user participation and create viral content. For example, #ShotOnOnePlus has been a successful campaign for OnePlus, showcasing the photography capabilities of its smartphones through user-generated content.
- Influencer Marketing: Partnering with influential figures in the tech and lifestyle space can significantly amplify a brand’s reach and credibility. Brands often collaborate with influencers to review their products, create unboxing videos, and promote special offers. For example, Samsung has partnered with numerous tech influencers to promote its Galaxy devices, leveraging their expertise and large followings.
- Live Streaming: Live streaming events on platforms like YouTube and Facebook allow brands to connect with their audience in real-time, providing exclusive product demos, behind-the-scenes insights, and interactive Q&A sessions. For example, Apple uses live streaming to unveil new iPhone models and showcase its latest software features.
Celebrity Endorsements
Celebrity endorsements are a popular marketing strategy for smartphone brands, leveraging the star power and influence of celebrities to appeal to a wider audience.
- Brand Ambassadors: Brands often appoint celebrities as brand ambassadors, associating their products with the celebrity’s image and lifestyle. For example, Samsung has collaborated with renowned actors and musicians to promote its Galaxy smartphones, leveraging their global recognition and appeal.
- Product Placement: Featuring smartphones in popular movies, TV shows, and music videos can subtly promote the brand and create a sense of desirability among viewers. For example, Apple has strategically placed its iPhones in numerous Hollywood blockbusters, associating its products with luxury and status.
Competitive Landscape and Industry Dynamics
The smartphone industry is a highly competitive landscape characterized by rapid technological advancements, evolving consumer preferences, and intense rivalry among key players. This dynamic environment necessitates a constant adaptation of strategies to maintain relevance and secure market share.
The smartphone industry is dominated by a few major players who collectively account for a significant portion of global shipments. These include:
- Apple: Renowned for its premium devices, user experience, and strong brand loyalty, Apple holds a significant market share, particularly in the high-end segment.
- Samsung: Samsung is the world’s largest smartphone manufacturer, known for its diverse product portfolio, from budget-friendly to high-end devices, catering to a wide range of consumers.
- Xiaomi: A rapidly growing Chinese manufacturer, Xiaomi has gained popularity for its affordable yet feature-rich devices, particularly in emerging markets.
- Oppo and Vivo: These Chinese brands have established a strong presence in Asia and are expanding globally, focusing on innovative camera technologies and stylish designs.
- Google: Google’s Pixel series focuses on software integration and user experience, competing in the premium segment with a loyal following.
Competitive Strategies, Smartphones brands
These players employ various strategies to differentiate themselves and gain a competitive edge:
- Product Innovation: Continuously developing new features, hardware improvements, and software enhancements to stay ahead of the competition.
- Pricing Strategies: Offering a range of price points to cater to different budgets and consumer segments, from budget-friendly options to high-end premium devices.
- Brand Building and Marketing: Investing heavily in branding, advertising, and marketing campaigns to build brand awareness and loyalty.
- Distribution and Sales Channels: Establishing strong partnerships with retailers, carriers, and online marketplaces to ensure widespread availability.
- Software and Ecosystem: Building robust software ecosystems with app stores, cloud services, and integrated experiences to enhance user engagement.
Industry Dynamics
Several factors drive the dynamics of the smartphone industry:
- Technological Advancements: The industry is constantly evolving with advancements in processor speeds, display technologies, camera capabilities, and battery life.
- Consumer Preferences: Consumers’ expectations are constantly changing, driven by factors like design trends, user experience, and specific features.
- Regulatory Changes: Government regulations regarding data privacy, security, and competition can impact industry practices and strategies.
- Economic Conditions: Economic factors, such as global economic downturns, can affect consumer spending and demand for smartphones.
- Emerging Markets: The growth of emerging markets presents new opportunities for smartphone manufacturers, particularly in regions with increasing smartphone penetration.
Competitive Landscape Table
| Competitor | Strengths | Weaknesses | Strategic Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apple | Strong brand loyalty, premium devices, seamless user experience, robust ecosystem | High price point, limited customization options, closed ecosystem | Maintaining premium positioning, expanding into emerging markets, focus on innovation and user experience |
| Samsung | Wide product portfolio, strong brand recognition, advanced display technologies, extensive distribution network | Competition from Chinese brands in mid-range segment, software updates can be slow | Maintaining market leadership, expanding into new segments, focusing on foldable and premium devices |
| Xiaomi | Affordable devices with high-end features, aggressive pricing strategy, strong presence in emerging markets | Software experience can be less polished, reliance on third-party components | Expanding globally, maintaining affordability, focusing on innovation and value for money |
| Oppo and Vivo | Innovative camera technologies, stylish designs, strong marketing campaigns, significant presence in Asia | Limited global reach, reliance on Chinese market, potential for brand dilution | Expanding globally, focusing on premium features and design, building brand awareness |
| Software integration, user experience, strong focus on artificial intelligence, competitive pricing | Limited hardware customization, smaller market share compared to other players | Maintaining focus on software and user experience, expanding into new segments, competing in the premium segment |
Emerging Smartphone Brands: Smartphones Brands
The smartphone market is not just dominated by the usual suspects. A wave of new players is challenging the established order, bringing fresh ideas and innovative features to the table. These emerging brands are carving their own niches and capturing the attention of consumers seeking alternatives to the mainstream.
Unique Offerings and Target Audiences
Emerging smartphone brands often succeed by focusing on specific target audiences and offering unique value propositions. They understand that consumers are looking for more than just the latest and greatest specs; they want devices that cater to their individual needs and lifestyles.
- Focus on affordability: Brands like Realme, Poco, and Redmi have gained popularity by offering powerful smartphones at competitive prices, appealing to budget-conscious consumers. These brands often prioritize core features like performance, camera quality, and battery life while keeping costs down.
- Niche features and functionalities: Some emerging brands focus on specific niches, like gaming, photography, or durability. For example, Asus ROG Phone series caters to gamers with its high refresh rate displays, powerful processors, and dedicated gaming features. Similarly, brands like CAT phones specialize in ruggedized smartphones designed for outdoor enthusiasts and professionals working in demanding environments.
- Sustainable and ethical practices: Consumers are increasingly aware of environmental and social issues, and some emerging brands are capitalizing on this trend by emphasizing sustainability and ethical sourcing. Fairphone, for instance, focuses on modularity and repairability, reducing electronic waste and promoting responsible manufacturing practices.
Growth Potential and Success Strategies
Emerging smartphone brands have several avenues for growth, including:
- Expanding into new markets: Many emerging brands are aggressively expanding into developing markets where smartphone penetration is still growing. These markets offer significant growth potential, especially for brands offering affordable and feature-rich devices.
- Building strong online presence: Emerging brands leverage online platforms like e-commerce websites and social media to connect directly with consumers and build brand loyalty. This approach allows them to bypass traditional retail channels and reach a wider audience.
- Partnerships and collaborations: Emerging brands often collaborate with other companies to leverage their expertise and reach. For example, they might partner with software developers to create exclusive apps or with retailers to offer bundled deals.
- Focus on innovation: To stand out from the competition, emerging brands need to continuously innovate and introduce new features and technologies. This could include developing cutting-edge camera systems, advanced AI capabilities, or unique design elements.
Examples of Successful Strategies
Several emerging smartphone brands have successfully challenged established players by adopting innovative strategies:
- Realme: Realme has gained significant market share by offering high-performance smartphones at competitive prices. Their aggressive marketing campaigns, strong online presence, and focus on key features have resonated with budget-conscious consumers.
- OnePlus: OnePlus initially gained traction by focusing on premium features and software experience at competitive prices. They built a strong community around their brand through online forums and social media, creating a sense of exclusivity and loyalty among their users.
- Nothing: Nothing has captured attention with its unique design language and focus on transparency. Their first smartphone, the Nothing Phone (1), features a transparent back panel with customizable LED lights, creating a distinctive visual identity.
Last Word
The smartphone industry is a dynamic and ever-changing landscape, where innovation, competition, and consumer preferences constantly shape the market. As we look towards the future, we can expect even more groundbreaking advancements in technology, pushing the boundaries of what smartphones can do and how they integrate into our lives. Understanding the forces that drive this industry is essential for anyone seeking to navigate the world of smartphones, whether as a consumer, an industry professional, or simply a curious observer.
The smartphone market is fiercely competitive, with brands like Apple, Samsung, and Google vying for market share. Developing a successful smartphone business requires a solid plan, and a comprehensive guide like Smartphone Business Plan: A Comprehensive Guide can provide valuable insights.
This guide covers everything from market analysis to financial projections, helping you navigate the complex world of smartphone brands and establish a successful venture.
 Informatif Berita Informatif Terbaru
Informatif Berita Informatif Terbaru