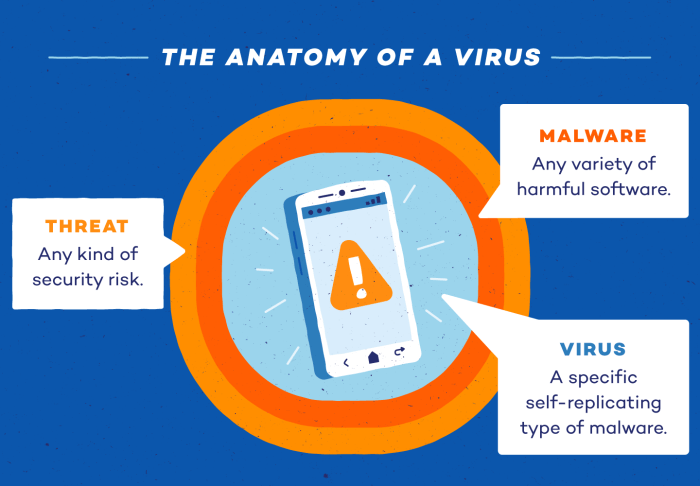
Smartphone viruses, a silent threat lurking in the digital landscape, have become increasingly prevalent, posing a significant risk to both individuals and businesses. These malicious programs, designed to infiltrate and compromise mobile devices, can steal sensitive data, disrupt operations, and leave users vulnerable to financial loss.
The rise of smartphone viruses can be attributed to the increasing reliance on mobile devices for communication, banking, and other critical activities. As our lives become more intertwined with our smartphones, the need for robust security measures becomes paramount. Understanding the nature of these threats, their methods of transmission, and the steps we can take to protect ourselves is crucial in safeguarding our digital well-being.
How Smartphone Viruses Spread
Smartphone viruses, also known as mobile malware, can spread through various methods, often exploiting vulnerabilities in operating systems and user behavior. Understanding these methods is crucial for protecting your device and personal information.
Methods of Virus Transmission, Smartphone viruses
Smartphone viruses can spread through multiple channels, including:
- Malicious Apps: These apps, disguised as legitimate ones, can contain hidden code that steals your data, tracks your activity, or displays unwanted ads. Some common examples include fake antivirus apps, game cheat apps, and apps offering free premium services.
- Infected Files: Downloading and opening infected files, such as APKs (Android Package Kit) or ZIP files, can introduce malware to your device. Be cautious about downloading files from unknown sources or clicking on suspicious links.
- SMS and MMS Messages: These messages can contain malicious links or attachments that, when clicked or opened, install malware on your device.
- Bluetooth: Malware can spread through Bluetooth connections, especially when devices are paired without proper security measures.
- Wi-Fi Networks: Connecting to public Wi-Fi networks without using a VPN can expose your device to malware attacks, as these networks are often unsecured and can be easily compromised.
Social Engineering Techniques
Social engineering tactics are often used to trick users into installing malware or providing sensitive information. Some common techniques include:
- Phishing: Attackers send fake emails or messages pretending to be from legitimate organizations, like banks or social media platforms, to lure users into clicking on malicious links or providing personal information.
- Baiting: Attackers offer tempting downloads or free services to entice users to install malware. These offers may appear legitimate, but they often lead to the installation of harmful software.
- Pretexting: Attackers create a believable scenario to gain trust and convince users to share personal information. This can involve impersonating authority figures or creating a sense of urgency.
Examples of Malicious Apps
Here are some examples of malicious apps that have been known to spread smartphone viruses:
- Fake Antivirus Apps: These apps claim to protect your device from viruses, but they often contain malware themselves, stealing your data or displaying intrusive ads.
- Game Cheat Apps: These apps promise to provide an unfair advantage in games, but they often install malware that can steal your account information or compromise your device.
- Free Premium Apps: These apps offer free access to premium services, such as streaming music or movies, but they often contain malware that can track your activity or steal your personal information.
Protecting Your Smartphone: Smartphone Viruses
Smartphones have become indispensable tools for communication, entertainment, and work. They hold sensitive personal information, including financial data, passwords, and contacts. Therefore, it’s crucial to protect your smartphone from malicious software, commonly known as viruses.
Choosing Secure Apps and App Stores
Choosing apps from reputable sources and understanding their permissions is essential to safeguard your smartphone.
- Download apps from official app stores: The Google Play Store and Apple App Store have strict guidelines for app developers, helping to filter out malicious apps. Avoid downloading apps from unknown sources or third-party websites.
- Read app reviews: Before installing an app, check user reviews to get insights into its functionality, security, and potential issues. Negative reviews often highlight red flags about app security or privacy concerns.
- Pay attention to app permissions: Apps request access to various phone features and data. Carefully review the permissions an app requires and deny access to sensitive information if it’s not necessary for the app’s core functionality. For example, a flashlight app shouldn’t need access to your contacts or location.
Regularly Updating Your Operating System and Security Software
Regular updates ensure your phone has the latest security patches to protect against newly discovered vulnerabilities.
- Update your operating system: Software updates often include security patches that address vulnerabilities exploited by viruses. Enable automatic updates on your phone to ensure you’re always running the latest version.
- Use reputable antivirus software: Installing a reputable antivirus app can provide real-time protection against malware and other threats. These apps scan for suspicious activity, detect malware, and remove it from your phone. Choose an antivirus app with a good reputation and positive user reviews.
Removing Smartphone Viruses
If you suspect your smartphone has been infected with a virus, it’s important to take action to remove it as soon as possible. Viruses can steal your personal information, damage your device, and slow down its performance.
Using Antivirus Software
Antivirus software is a valuable tool for detecting and removing smartphone viruses. These programs scan your device for malicious software and can quarantine or remove any threats they find.
- Choose a reputable antivirus app from a trusted source, such as the Google Play Store or Apple App Store.
- Install and run the antivirus app on your smartphone. It will scan your device for viruses and other threats.
- Follow the app’s instructions to remove any detected viruses.
Restoring Your Smartphone to Factory Settings
If antivirus software is unable to remove the virus, you may need to restore your smartphone to its factory settings. This will erase all data on your device, including your apps, photos, and other files.
- Before restoring your smartphone to factory settings, back up your important data to a cloud storage service or an external hard drive. This will ensure you don’t lose any valuable information.
- Go to your smartphone’s settings menu and find the “Backup & Reset” or “Factory Data Reset” option.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to reset your smartphone to its factory settings.
Case Studies of Smartphone Virus Attacks
Smartphone viruses, while often less publicized than their computer counterparts, can be equally damaging. Understanding real-world examples of these attacks helps us learn from past mistakes and strengthen our defenses.
Notable Smartphone Virus Attacks
These attacks highlight the evolving nature of smartphone malware and the importance of staying informed and vigilant.
| Virus Name | Year | Impact | Affected Devices | Lessons Learned |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gooligan | 2016 | Stole Google accounts, granting attackers access to sensitive data and financial information. | Android devices | The attack exposed vulnerabilities in Android’s security system, emphasizing the need for regular updates and robust security measures. |
| HummingBad | 2016 | Installed malicious apps without user consent, generating revenue through fraudulent clicks and downloads. | Android devices | This attack highlighted the dangers of downloading apps from untrusted sources and the importance of verifying app permissions. |
| Skygofree | 2017 | Spied on users by recording calls, stealing data, and accessing sensitive information. | Android devices | This attack emphasized the importance of being cautious about clicking on suspicious links and the need for comprehensive mobile security solutions. |
| Agent Smith | 2019 | Replaced legitimate apps with malicious versions, stealing user data and generating revenue through fraudulent activities. | Android devices | This attack underscored the importance of verifying app authenticity and downloading apps from trusted sources. |
End of Discussion
In the ever-evolving world of mobile technology, staying vigilant against smartphone viruses is essential. By adopting a proactive approach to security, including regularly updating software, choosing reputable apps, and being cautious of suspicious links, we can mitigate the risks and protect our devices from malicious attacks. As technology advances, so too will the tactics employed by cybercriminals. It is imperative to remain informed about emerging threats and adapt our security practices accordingly to ensure a safe and secure mobile experience.
Smartphone viruses can be a real headache, and often sneak in through apps downloaded from sources other than official app stores. To help protect users, Samsung has added a new sideloading restriction to Galaxy smartphones , making it harder to install apps from unknown sources.
This new restriction should help to reduce the risk of your phone becoming infected with malware, keeping your personal information safe.
 Informatif Berita Informatif Terbaru
Informatif Berita Informatif Terbaru