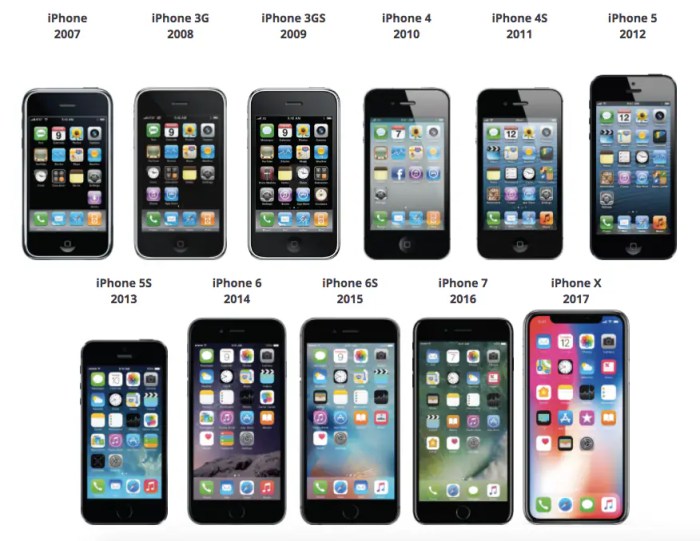
All smartphones, from the first rudimentary models to the sleek, powerful devices we carry today, have revolutionized the way we live, work, and connect. This journey through the history, technology, and impact of smartphones reveals a captivating narrative of innovation, evolution, and the ever-expanding possibilities of mobile technology.
From the early days of basic communication to the modern era of sophisticated apps, high-resolution cameras, and ubiquitous connectivity, smartphones have become an integral part of our lives. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of these devices, exploring their design, hardware, software, and the ever-evolving landscape of the smartphone industry.
The Evolution of Smartphones
The journey of the smartphone from its humble beginnings to its current ubiquitous presence is a testament to the relentless pace of technological advancement. This evolution is marked by key milestones, each bringing about significant changes in design, features, and capabilities, ultimately transforming the way we communicate, access information, and interact with the world.
Early Pioneers: The Birth of Smartphones
The first smartphones emerged in the late 1990s and early 2000s, building upon the foundation laid by mobile phones and personal digital assistants (PDAs). These early models were bulky, expensive, and limited in functionality.
- IBM Simon Personal Communicator (1994): Often cited as the first true smartphone, the IBM Simon combined a mobile phone with a touchscreen PDA, enabling users to make calls, send faxes, send emails, and even play simple games.
- Nokia Communicator 9000 (1996): This device introduced a clamshell design with a physical keyboard and a small monochrome display. It offered more advanced features than the Simon, including a web browser and email capabilities.
- BlackBerry 850 (1999): This device revolutionized mobile communication with its focus on email and messaging. The BlackBerry’s physical keyboard and push email service made it a popular choice for business professionals.
The Rise of Touchscreens and Mobile Operating Systems
The introduction of touchscreen technology and mobile operating systems in the mid-2000s marked a turning point in the evolution of smartphones. These advancements paved the way for a more intuitive user experience and opened up possibilities for a wider range of applications.
- Apple iPhone (2007): The iPhone, with its multi-touch display, sleek design, and App Store, revolutionized the smartphone industry. It introduced a new paradigm for mobile computing, emphasizing user-friendliness and a focus on applications.
- Android (2008): Google’s Android operating system brought an open-source platform to the smartphone market, fostering a vibrant ecosystem of developers and manufacturers. This led to a diverse range of Android devices, catering to different needs and budgets.
The Era of Smartphones: Features and Capabilities
The smartphone landscape has become increasingly diverse and sophisticated, with manufacturers constantly pushing the boundaries of innovation. Today’s smartphones boast an array of advanced features, including:
- High-resolution displays: Smartphones now offer stunning visual experiences with high-resolution displays, vibrant colors, and improved pixel density.
- Powerful processors: Advancements in chip technology have resulted in smartphones with incredibly powerful processors, capable of handling demanding tasks such as gaming and video editing.
- Advanced cameras: Smartphone cameras have become remarkably sophisticated, offering features like multiple lenses, optical zoom, and AI-powered image processing, enabling users to capture professional-quality photos and videos.
- 5G connectivity: The rollout of 5G networks has brought about a significant increase in mobile data speeds, enabling faster downloads, smoother streaming, and more responsive online experiences.
- Artificial intelligence (AI): AI is being integrated into smartphones to enhance various functionalities, such as voice assistants, image recognition, and personalized recommendations.
The Future of Smartphones: Emerging Trends
The evolution of smartphones continues, driven by ongoing technological advancements and evolving user needs. Some key trends shaping the future of smartphones include:
- Foldable and flexible displays: Smartphones with foldable and flexible displays offer a larger screen experience without sacrificing portability. This trend is poised to transform the way we interact with our devices.
- Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR): AR and VR technologies are being integrated into smartphones to create immersive experiences and enhance everyday tasks. For example, AR can be used for navigation, shopping, and entertainment, while VR can offer interactive gaming and virtual experiences.
- Biometric authentication: Smartphones are increasingly incorporating biometric authentication methods, such as facial recognition and fingerprint scanning, to enhance security and provide a more convenient user experience.
- Sustainable design: As environmental concerns grow, smartphone manufacturers are focusing on sustainable design principles, using recycled materials and reducing energy consumption.
Smartphone Operating Systems: All Smartphones
The operating system (OS) is the software that controls the hardware and software of a smartphone. It provides the user interface, manages applications, and ensures smooth operation. Smartphone operating systems are the foundation upon which all other applications and functionalities are built.
Comparison of Major Smartphone Operating Systems
The major smartphone operating systems are Android, iOS, and Windows Phone. Each OS has its own strengths and weaknesses, catering to different user preferences and needs.
- Android is an open-source operating system developed by Google. It is known for its flexibility, customization options, and wide range of apps available on the Google Play Store. It powers a vast majority of smartphones globally, thanks to its open-source nature, allowing manufacturers to customize and tailor it to their devices. Android’s open nature allows for a vibrant ecosystem of developers and app creators, contributing to a diverse app library.
- iOS is a closed-source operating system developed by Apple. It is known for its user-friendly interface, tight integration with Apple’s ecosystem, and robust security features. iOS devices are known for their high-quality hardware and software integration, offering a seamless user experience. The controlled environment of iOS ensures a consistent and secure platform for users.
- Windows Phone was a mobile operating system developed by Microsoft. While it had a strong focus on integration with Microsoft services and a unique tile-based interface, it struggled to gain significant market share and was discontinued in 2017. Its user base was relatively small compared to Android and iOS, limiting its reach and app availability.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Operating System
Each operating system has its own unique advantages and disadvantages, which influence user preference and market adoption.
- Android:
- Advantages: Open-source, customizable, wide app selection, affordable devices.
- Disadvantages: Can be fragmented, security concerns, bloatware on some devices.
- iOS:
- Advantages: User-friendly, secure, tight integration with Apple ecosystem, high-quality hardware.
- Disadvantages: Limited customization, expensive devices, closed ecosystem, app exclusivity.
- Windows Phone:
- Advantages: Seamless integration with Microsoft services, unique tile-based interface.
- Disadvantages: Limited app availability, small market share, discontinued.
The market share of each operating system reflects its popularity and influence on the smartphone industry.
- Android holds the largest market share globally, dominating the smartphone market with its open-source nature and wide device availability.
- iOS holds a significant market share, primarily in developed markets, known for its premium devices and user experience.
- Windows Phone, despite its discontinuation, had a limited impact on the smartphone industry due to its small market share and limited app ecosystem.
Smartphone Applications and Software
Smartphone applications, or apps, have become an integral part of modern life, transforming how we communicate, work, learn, and entertain ourselves. From social media to productivity tools, entertainment platforms, and more, apps have revolutionized the way we interact with technology and the world around us.
Types of Smartphone Applications
Smartphone applications can be broadly categorized based on their functionality and purpose. Some of the most common types of apps include:
- Social Media Apps: These apps facilitate social interaction and connection, enabling users to share updates, photos, videos, and messages with friends, family, and followers. Examples include Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and TikTok.
- Communication Apps: These apps allow users to communicate with others through various means, including messaging, voice calls, and video calls. Popular examples include WhatsApp, Messenger, Telegram, and Skype.
- Productivity Apps: Designed to enhance efficiency and productivity, these apps offer tools for tasks such as note-taking, task management, email, calendar scheduling, and document editing. Popular examples include Google Workspace, Microsoft Office, Evernote, and Trello.
- Entertainment Apps: These apps provide access to entertainment content, including music streaming, video streaming, gaming, and news. Examples include Spotify, Netflix, YouTube, and Amazon Prime Video.
- Games: Smartphone gaming has become increasingly popular, with a wide range of games available, from casual puzzle games to complex action-adventure titles. Examples include Candy Crush Saga, Clash of Clans, PUBG Mobile, and Call of Duty Mobile.
- Navigation Apps: These apps provide real-time navigation assistance, helping users find their way around using GPS and mapping technology. Popular examples include Google Maps, Waze, and Apple Maps.
- Shopping Apps: These apps allow users to browse, purchase, and manage their online shopping needs. Examples include Amazon, eBay, and AliExpress.
- Financial Apps: These apps provide tools for managing personal finances, including banking, budgeting, and investing. Examples include Mint, Personal Capital, and Robinhood.
- Health and Fitness Apps: These apps help users track their health and fitness goals, offering features such as activity tracking, calorie counting, and sleep monitoring. Examples include Fitbit, MyFitnessPal, and Headspace.
Impact of Mobile Apps on User Behavior and Daily Life
Smartphone applications have significantly impacted user behavior and daily life, influencing how we interact with information, communicate, and manage our time.
- Increased Connectivity and Communication: Mobile apps have made it easier than ever to stay connected with friends, family, and colleagues, regardless of location.
- Enhanced Information Access: Apps provide instant access to a vast amount of information, from news and weather updates to educational resources and entertainment content.
- Convenience and Efficiency: Mobile apps streamline daily tasks, such as shopping, banking, transportation, and scheduling, making life more convenient and efficient.
- Personalized Experiences: Apps often use data and algorithms to personalize user experiences, offering tailored recommendations and content based on individual preferences.
- Social and Cultural Impact: Mobile apps have played a significant role in shaping social trends, influencing communication styles, and creating new forms of entertainment and interaction.
Business Models and Revenue Streams of Popular Smartphone Apps, All smartphones
Smartphone apps have become a significant revenue-generating industry, with various business models and revenue streams employed by app developers.
- Freemium Model: This model offers a basic version of the app for free, with additional features or content available for purchase through in-app purchases. Examples include Spotify, Candy Crush Saga, and many mobile games.
- Subscription Model: Users pay a recurring fee to access premium features or content, such as ad-free experiences, exclusive content, or additional functionality. Examples include Netflix, Spotify Premium, and Adobe Creative Cloud.
- In-App Advertising: Apps generate revenue by displaying ads to users, typically in the form of banner ads, video ads, or interstitial ads. Examples include many free-to-play games, social media apps, and news apps.
- Transaction Fees: Some apps, such as e-commerce platforms and ride-sharing services, earn revenue by charging a commission on transactions made through the app.
- Data Collection and Monetization: Apps may collect user data, such as browsing history, location data, and app usage patterns, and use this data to target advertising or sell it to third-party companies.
Smartphone Industry and Market Trends
The global smartphone market is a dynamic and rapidly evolving industry, driven by technological advancements, consumer preferences, and economic factors. This section will explore the key trends shaping the smartphone industry, analyzing its size, growth, and major players. Additionally, we will examine the impact of emerging technologies like foldable phones, 5G, and artificial intelligence on the smartphone landscape. Finally, we will delve into potential future trends and their implications for the market.
Global Smartphone Market Size and Growth
The global smartphone market is a multi-billion dollar industry, with annual shipments exceeding 1.3 billion units in recent years. The market has experienced significant growth over the past decade, driven by factors such as increasing smartphone affordability, rising internet penetration, and the growing demand for mobile applications and services.
The market is expected to continue growing in the coming years, albeit at a slower pace than in the past. Research firm IDC forecasts that global smartphone shipments will reach 1.4 billion units by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.5%.
Key Players in the Smartphone Industry
The global smartphone market is dominated by a few key players, including:
- Samsung: The South Korean electronics giant is the world’s largest smartphone manufacturer, holding a significant market share. Samsung is known for its flagship Galaxy series, which includes high-end models like the Galaxy S and Galaxy Note, as well as more affordable options like the Galaxy A series.
- Apple: The American technology company is a major player in the premium smartphone segment. Apple’s iPhone lineup, known for its sleek design, user-friendly interface, and strong ecosystem, enjoys a loyal customer base.
- Xiaomi: The Chinese technology company has emerged as a leading smartphone manufacturer, particularly in emerging markets. Xiaomi is known for its affordable devices with high-end features and a focus on innovation.
- Oppo: Another Chinese technology company, Oppo has gained significant market share in recent years, particularly in Asia. Oppo is known for its camera-centric smartphones and stylish designs.
- Vivo: A subsidiary of BBK Electronics, Vivo is a major player in the Chinese smartphone market. Vivo is known for its innovative features, such as its under-display fingerprint sensor technology.
Impact of Emerging Trends on the Smartphone Industry
Several emerging trends are transforming the smartphone industry, including:
Foldable Phones
Foldable phones offer a unique combination of portability and a larger screen experience. These devices are still in their early stages of development, but they have the potential to disrupt the smartphone market by offering a new form factor and enhanced functionality.
5G Technology
The rollout of 5G networks is enabling faster download and upload speeds, lower latency, and greater bandwidth. This is opening up new possibilities for smartphone applications and services, such as mobile gaming, virtual reality (VR), and augmented reality (AR).
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is being integrated into smartphones to enhance various functionalities, including image recognition, voice assistants, and personalized recommendations. AI-powered features are making smartphones more intelligent and user-friendly.
Potential Future Trends in the Smartphone Industry
The smartphone industry is constantly evolving, and several trends are likely to shape the market in the coming years:
Advancements in Display Technology
Displays are a key component of the smartphone experience, and advancements in display technology are expected to continue. This includes higher resolutions, improved refresh rates, and foldable displays.
Improved Battery Life
Battery life is a critical factor for smartphone users, and advancements in battery technology are expected to lead to longer battery life and faster charging times.
Enhanced Security Features
Security is becoming increasingly important for smartphone users, and advancements in biometric authentication, such as facial recognition and in-display fingerprint sensors, are expected to enhance security features.
Integration of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
AR and VR technologies are gaining traction in the smartphone market, and they are expected to be integrated into more devices in the future. This could lead to new and immersive experiences for users.
Growth of the Internet of Things (IoT)
The IoT is a network of interconnected devices, and smartphones are playing a key role in this ecosystem. As the IoT grows, smartphones are expected to become more connected and integrated with other devices.
The smartphone industry is constantly evolving, and these trends are likely to shape the market in the coming years.
Smartphone Photography and Videography
The rise of smartphones has revolutionized photography and videography, making high-quality image and video capture accessible to everyone. The evolution of smartphone cameras has been remarkable, from basic point-and-shoot functionality to advanced features that rival dedicated cameras.
The Evolution of Smartphone Cameras
The capabilities of smartphone cameras have significantly advanced over time, driven by innovations in hardware and software.
- Early Smartphones (2000s): The first smartphones featured rudimentary cameras with low resolutions and limited functionality.
- The Rise of Megapixels (2010s): The focus shifted to increasing megapixel count, leading to sharper images and better zoom capabilities.
- Advanced Image Processing (2010s-Present): Smartphone cameras began incorporating advanced image processing algorithms to enhance image quality, reduce noise, and improve dynamic range.
- Multiple Lenses and Computational Photography (Present): Modern smartphones feature multiple lenses, including wide-angle, telephoto, and macro lenses, allowing for diverse perspectives. Computational photography techniques, such as HDR (High Dynamic Range) and AI-powered scene recognition, further enhance image quality.
Impact on Photography and Videography
Smartphone photography has had a profound impact on the world of photography and videography, democratizing image capture and fostering creativity.
- Increased Accessibility: Smartphones have made photography and videography accessible to a wider audience, empowering individuals to document their lives and share their experiences.
- Growth of Mobile Photography Communities: Online platforms and social media have created thriving communities of smartphone photographers, sharing tips, techniques, and inspiring each other.
- New Perspectives and Styles: The versatility of smartphones has encouraged experimentation with different perspectives, angles, and creative approaches to image capture.
- Impact on Professional Photography: While smartphones have not replaced professional cameras, they have influenced the industry by driving innovation and pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
Techniques for High-Quality Smartphone Photography and Videography
Capturing high-quality images and videos with a smartphone requires understanding and applying specific techniques and strategies.
- Composition: Apply the rules of composition, such as the rule of thirds, leading lines, and balance, to create visually appealing images.
- Lighting: Pay attention to lighting conditions, using natural light whenever possible. Avoid harsh shadows and backlighting, and consider using external light sources when needed.
- Focus and Exposure: Focus carefully on your subject, and adjust exposure settings to achieve optimal brightness and contrast.
- Stability: Use a tripod or other stabilizing device to minimize camera shake, especially in low-light conditions or when shooting video.
- Editing: Enhance your images and videos using editing apps to adjust brightness, contrast, color, and other parameters.
The Future of Smartphones
Smartphones have become an indispensable part of our lives, transforming the way we communicate, access information, and interact with the world around us. As technology continues to evolve at an unprecedented pace, the future of smartphones promises even more transformative possibilities, blurring the lines between the physical and digital realms.
Emerging Technologies Shaping the Smartphone Experience
Emerging technologies like augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) have the potential to revolutionize the smartphone experience, offering new ways to interact with the world and access information.
- Augmented Reality (AR): AR overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing our perception of reality. Smartphones equipped with advanced AR capabilities can provide real-time information about our surroundings, such as directions, product details, or historical facts. AR can also be used for interactive games, virtual shopping experiences, and remote assistance. For example, imagine using your smartphone to see the interior design of a piece of furniture in your living room before purchasing it, or to get step-by-step instructions for assembling a product overlaid on the actual object.
- Virtual Reality (VR): VR immerses users in a simulated environment, creating a sense of presence and interaction. Smartphones can be used to access VR experiences through dedicated headsets, offering a wide range of applications, including gaming, entertainment, education, and training. For instance, a VR experience on your smartphone could allow you to explore ancient ruins, visit distant planets, or attend virtual concerts.
- Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs): BCIs enable communication between the brain and external devices, opening up possibilities for controlling smartphones with our thoughts. While still in its early stages, BCI technology could allow us to make calls, send messages, or navigate apps without physically touching our phones. Imagine controlling your smartphone to play music, adjust the volume, or change the channel simply by thinking about it.
Final Conclusion
As we stand at the cusp of a new era in mobile technology, it’s clear that smartphones will continue to shape our world in profound ways. From the integration of artificial intelligence to the advent of foldable displays and 5G networks, the future of smartphones promises even more exciting innovations that will further enhance our lives and redefine the boundaries of what’s possible.
All smartphones are constantly evolving, offering a wide range of features and functionalities. It can be overwhelming to choose the right one for your needs, especially when considering the best smartphone 2023 picks. But ultimately, the ideal smartphone is the one that best suits your individual preferences and usage patterns.
 Informatif Berita Informatif Terbaru
Informatif Berita Informatif Terbaru